Hemodynamic monitoring provides us with information on cardiovascular performance and has therefore become a fundamental tool in the diagnostic approach and therapeutic orientation.
More and more devices are becoming available that allow us to carry out advanced monitoring, and it is sometimes difficult to choose between them.
WHAT WILL YOU FIND IN THIS ARTICLE?
- Things to consider when selecting a hemodynamic monitor.
- Maximum accuracy with the minimun invasiveness required.
- How to get a quality blood pressure waveform?
- Useful for all types of patients: neonatal, pediatric, adult, or veterinary.
- Parameters capable of assessing the patient’s complete hemodynamics: preload, afterload and contractility.
Do you want to know more about hemodynamic monitoring systems? Stay on this page and read the full entry.
More and more devices are becoming available that allows us to carry out advanced monitoring, and it is sometimes to choose between them.
Aspects to take into account when selecting a hemodynamic monitor
To be able to make an accurate reading of the hemodynamic status of patients, which allows us to direct treatment and anticipate possible complications, we will need a system that provides us with:
- Maximum precision with the minimum invasiveness necessary.
- Useful for all types of patients: neonatal, pediatric, adult or veterinary.
- Have parameters capable of assessing the complete hemodynamic of the patient: preload, afterload and contractility.
Accuracy and low invasivness – it is possible?
Hemodynamic monitoring in the intensive care unit (ICU) is considered essential for the management of critically ill patients.3 However, its use is not without risk, especially when considering the invasive nature of these procedures and their associated complications.1
So, when looking for the ideal hemodynamic monitor, we want it to be accurate yet minimally invasive – it is possible?
Advanced hemodynamic monitoring, what options do we have?
Effective and accurate hemodynamic monitoring can help in the early identification of cardiovascular inestability and the timely selection of the most appropiate therapeutic treatment.
In identifying the most appropiate system, invasiveness and accuracy are two essential aspects and are closely related to the way the systrm collects information.
Among the various advanced hemodynamic monitoring systems, the most widely used are those that analyse the pulse contour of the arterial pressure wave (PCM) to estimate systolyc volume, which are considered minimally invasive. In order to obtain accurate data, it os necessary to have a good quality arterial pressure wave, which is essential for systems based on pulse contour analysis. Therefore, a series of simple maneuvers should be carried out to prevent the wave from resonance or damping phenomena.
When it comes to accuracy, what needs to be taken into account is the type of calculation used to obtain the systolic volume (SV) and thus cardiovascular impedance.
On the one hand, we have hemodynamic monitoring systems using the laws of classical physics (Otto Frank’s law ans Stewart Hamilton’s law) which are more accurate than those based on statistical methods (Langewouters, Curtosi). In the latter, relying on predetermined data not taking individual hemodynamic differences into account, accuracy is inevitably low.
Statistical methods
Statistical methods are based on statistical calculation based on sampling of blood pressure and its standard deviations. They use data from healthy patients to correct the values obtained. This methods do not use the impedance of the cardiovascular system for the calculation of stroke volume.
They are minimally invasive or non-invasive. Their disadvantage is:
- Lower accuracy than those based on physical methods because the estimates are not made on the patient’s own data, but from pre-established data.
Physical methods
Systems based on physical methods include those usen termodilution, indicator dilution or perturbation theory.
Physical methods are accurate and reliable as they are validated for a large number of clinical situations.
The major drawback of these systems is their high invasiveness and the need for callibration, except for the P.R.A.M. method.
The P.R.A.M. method, unlike the thermodilution or indicator dilution methods, is minimally invasive, thus avoiding many of the potential complications than can arise from monitoring.
For accurate data, all methods based on pulse contour analysis will require a good quality of the arterial pressure waveform. This problem can be solved by performing a series of maneuvers or by using tools, such as the electronic filter found in systems like the P.R.A.M. method.
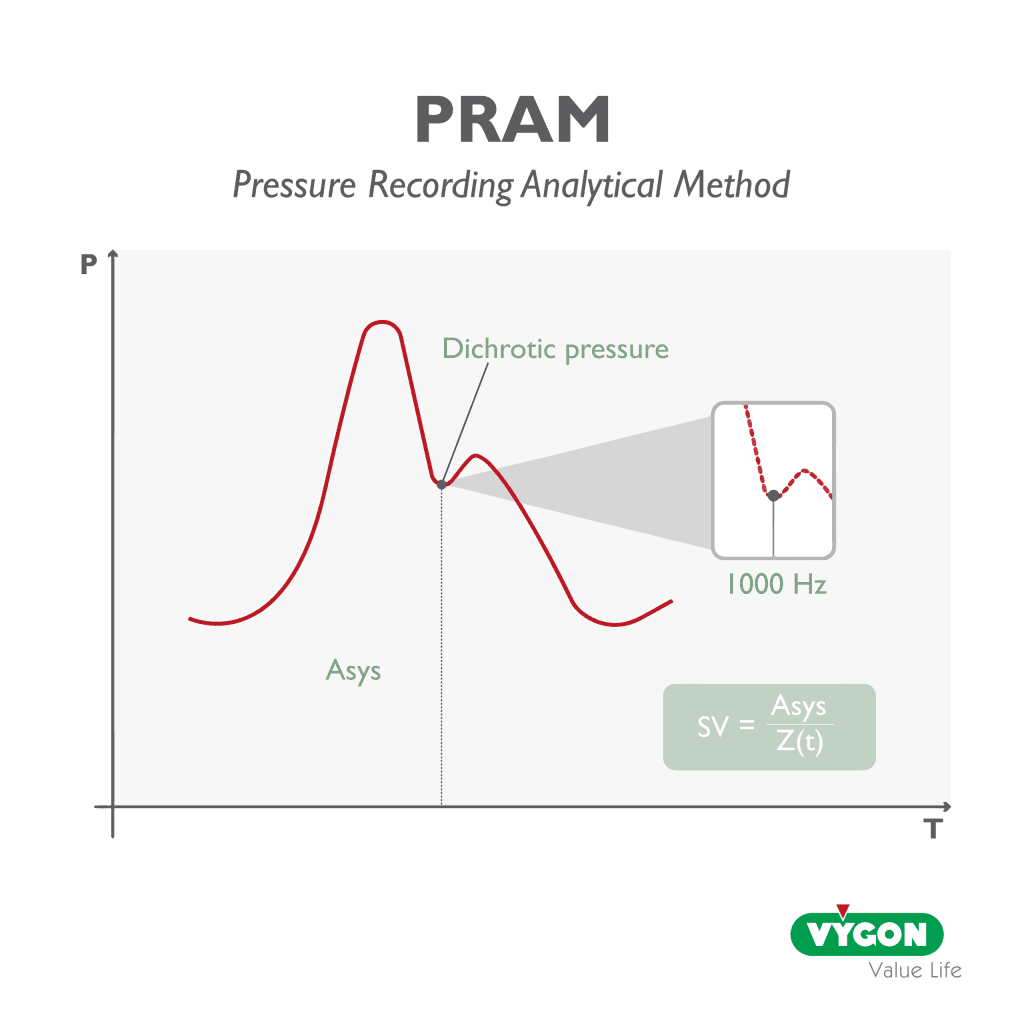
P.R.A.M. deduces the systolic outpud and other hemodynamic variables from analysis of the arterial pressure curve morphology alone, which it acquires accurately, sampling at a rate of 1000 Hz during each cardiac cycle, thus enabling continous monitoring that is sensitive to the slightest hemodynamic changes in the patient.
This means that every single arterial pulse is detected an analysed; every change in the patient’s state and every reaction to a stimulus by the operator is immediatly detected, analysed and provided in real time, beat by beat.
The uniqueness of P.R.A.M. lies in the method’s ability to calculate the characteristic impedance of the cardiovascular system (Z(t)) in real time, beat-to-beat and patient-specific for the entire cardiac cycle, considering not only the pulsatory phase, but also the continous flow phase.
Since impedance is constantly changing, this method does not use constant or prestimulated values for its calculation, precisely in order to reliably follow its pathophysiological variations.
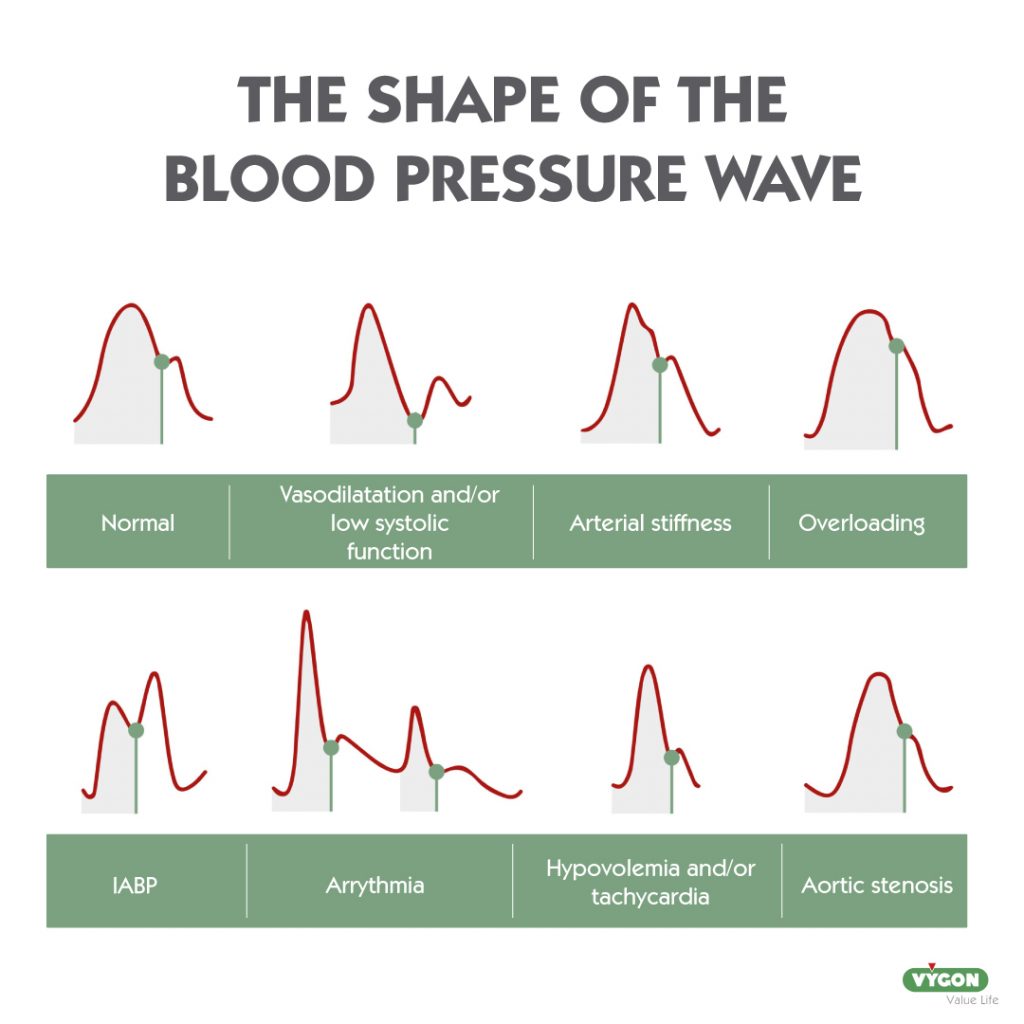
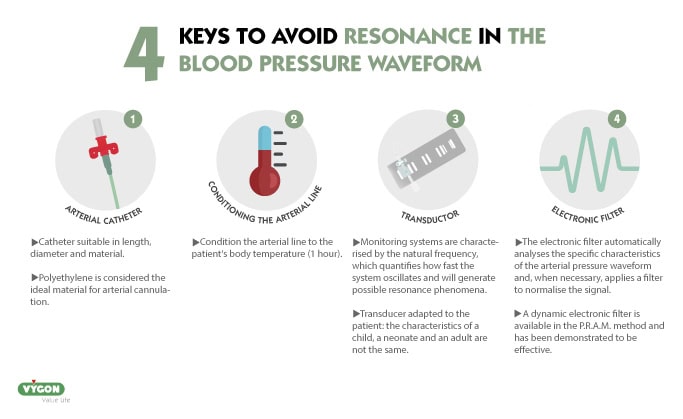
How to avoid artefacts in the arterial pressure waveform?
Good practices such as selecting the appropiate arterial catheter (length, diameter and material), conditioning line to body temperature or selecting a good quality transducer adapted to the patient will reduce the likehood of our waveform showing resonance or damping.
Resonant waveforms are common, so much so that in 30.7% os cases, the arterial pressure waveform is resonant. 11
In addition to the above strategies, there are also tools that can help us to correct our waveform so that it is as close as possible to the patient’s hemodynamic reality: the use of an electronic filter.
A dynamic electronic filter is available in the P.R.A.M. method, which has been validated and tested in studies, proving to be very useful in elliminating resonance.4
Useful for all types of patients: neonatal, pediatric, adult or veterinary
Is there a hemodynamic monitoring system that is suitable for all patients? The answer is yes, but it will need to be based on pulse contour analysis and not on preset data as is the case with statistical methods.
The estimation of arterial or cardiovascular impedance (Z) is key to the calculation of stroke volume and is the basis for the development of the mathematical algorithms of the different pulse contour analysis methods.
When the system performs a direct cardiovascular impedance (Z) calculation, it is possible to obtain reliable data independent of the physical characteristics of the patient.
The P.R.A.M. method meets these characteristics and is validated for adults, children and neonates, and is even capable of providing accurate data in veterinary medicine. It is the only estimation method based on pulse contour analysis that has been validated in pediatric patients against a reference method.5
Furthermore, it is validated for a multitude of clinical situations, including septic patients, where even after norepinephrine depletion and changes in vascular tone or volume expansion, the data have remained highly correlated with the reference system.12
The studies position the P.R.A.M. method as a:
“Reliable ans useful tool in emergency clinical settings where highly invasive devices are not immediately available.”12
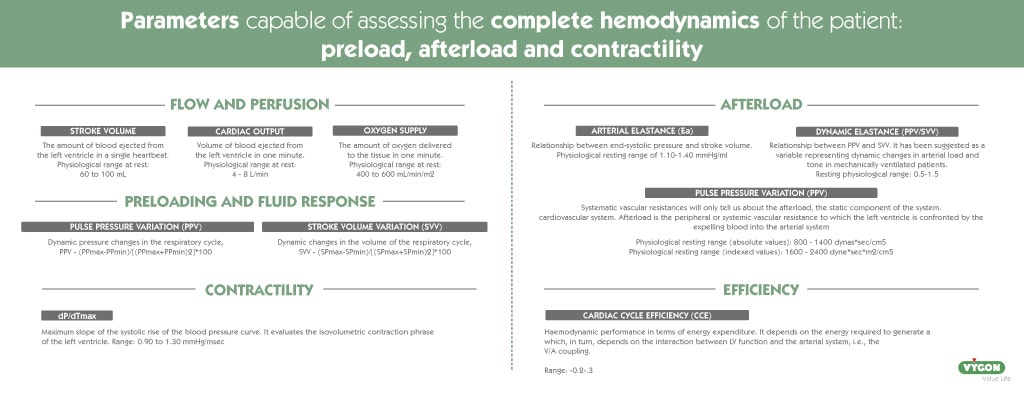
Parameters capable of assessing the complete hemodynamics of the patient: preload, afterload and contractility
In addition to the usual parameters such as systolic volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), oxygen delivery (DO2), pulse contour variation (PPV), systolic volume variation (SVV) or system vascular resistance (SVR), it os also interesting to have more advanced parameters that complement these and provide us with more information about the cardiovascular system.
Two variables that we could highlight for the information they provide would be: Cardiac Efficiency Cycle (CCE) or the dp/dt max.
DP/DT MAX
The dP/dt max refers to the maximum slope of the systolic rise of the arterial pressure curve.
This parameter is considered an indicator of myocardial contractility independent of preload, i.e. how the left ventricle contracts in the isovolumetric phase, before the aortic valve opens.
Therefore, it is the moment at which the left ventricle must exert maximum force or have maximum contractility to open the aortic valve.
When we observe unphysiological values of dP/dt max, above 1.6 mmHg/ml, it will indicate the presence of arterial resonance.
Cardiac cycle efficiency (cce)
Cardiac cycle efficiency (CCE) gives information about the amount of energy being axpended by the cardiovascular system to eject blood at each systole. When the system is efficient, the value is zero.
When we observe negative values, we can say that system is being inefficient.
There are multiple clinical reasons why the system mas be inefficient, such as hypovolemia, decreased contractility, increased afterload, tachycardia, bradycardia, etc.
CCE has been shown to be able to detect alterations in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and therefore may be a good tool to detect the need for echocardiography. CCE is capable to discriminate between normal, moderatly impaired, and markedly impaired LVEF with good sensitivity and specificity.13
However, regardless of the cause, whenever we observe negative values, we are dealing with global alteration of the system.
Therefore, when we observe that the CCE is altered, we know that something is happening in the cardiovascular system and we should evaluate this data together with complementary parameters. In this way, we will be able to analyse the cause and guide the treatmen.
In critically ill patients, hemoynamic monitoring is essential an will mostly determine the patient’s evolution an recovery. Therefore, it is great importance to have a hemodynamic monitor that provides us with accurate an real-time information.
Bibliographie
1. Pour-Ghaz, I., Manolukas, T., Foray, N., Raja, J., Rawal, A., Ibebuogu, U. N., & Khouzam, R. N. (2019). Accuracy of non-invasive and minimally invasive hemodynamic monitoring: where do we stand?. Annals of translational medicine, 7(17), 421. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.07.06
2. Rodríguez Sola, David. Fortes Díaz, Daniel. González Bernal, Melanie. Godoy García, José Eulogio (2021). Manejo de Enfermería de la monitorización hemodinámica continua invasiva en paciente crítico. Ocronos – Editorial Científico-Técnica. https://revistamedica.com/manejo-enfermeria-monitorizacion-hemodinamica-invasiva/#Complicaciones-inmediatas
3. Belda, F., Aguilar, G., Teboul, J., Pestaña, D., Redondo, F., Malbrain, M., Luis, J., Ramasco, F., Umgelter, A., Wendon, J., Kirov, M., & Fernández-Mondéjar, E. (2011). Complications related to less-invasive haemodynamic monitoring ‡. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 106(4), 482–486. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aeq377
4. Foti L, Michard F, Villa G, Ricci Z, Romagnoli S. The impact of arterial pressure waveform underdamping and resonance filters on cardiac output measurements with pulse wave analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2022 Jul;129(1):e6-e8. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2022.03.024. Epub 2022 Apr 19. PMID: 35459533.
5. Alonso-Iñigo JM, Escribá FJ, Carrasco JI, Fas MJ, Argente P, Galvis JM, Llopis JE. Measuring cardiac output in children undergoing cardiac catheterization: comparison between the Fick method and PRAM (pressure recording analytical method). Paediatr Anaesth. 2016 Nov;26(11):1097-1105. doi: 10.1111/pan.12997. Epub 2016 Aug 27. PMID: 27565740.
6. Quilis, Amadeo Almela., Millán Soria, Javier., Alonso Íñigo, José Miguel., García Bermejo, Pedro. (2015). Monitorización hemodinámica no invasiva o mínimamente invasiva en el paciente crítico en los servicios de urgencias y emergencias. Revista Científica de la Sociedad Española de Medicina de Urgencias y Emergencias. Vol. 27, n. 6. https://revistaemergencias.org/numeros-anteriores/volumen-27/numero-6/monitorizacion-hemodinamica-no-invasiva-o-minimamente-invasiva-en-el-paciente-critico-en-los-servicios-de-urgencias-y-emergencias/
7. Suess EM, Pinsky MR. Hemodynamic Monitoring for the Evaluation and Treatment of Shock: What Is the Current State of the Art? Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Dec;36(6):890-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1564874. Epub 2015 Nov 23. PMID: 26595049.
8. Chaney JC, Derdak S. Minimally invasive hemodynamic monitoring for the intensivist: current and emerging technology. Crit Care Med. 2002 Oct;30(10):2338-45. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200210000-00025. PMID: 12394965.
9. Moreno Sasig, N. G., Vélez Muentes, J. R., Campuzano Franco, M. A., Zambrano Córdova, J. R., & Vera Pinargote, R. G. (2021). Monitorización invasiva y no invasiva en pacientes ingresados a UCI. Análisis del comportamiento de las líneas de crédito a través de la corporación financiera nacional y su aporte al desarrollo de las PYMES en Guayaquil 2011-2015, 5(3), 278–292. https://doi.org/10.26820/recimundo/5.(2).julio.2021.278-292
10. Mateu Campos, M.L., Ferrándiz Sellés, A., Gruartmoner de Vera, G., Mesquida Febrer, J., Sabatier Cloarec, C., Poveda Hernández, Y., & García Nogales, X.. (2012). Técnicas disponibles de monitorización hemodinámica: Ventajas y limitaciones. Medicina Intensiva, 36(6), 434-444. https://dx.doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.medin.2012.05.003
11. Romagnoli S, Ricci Z, Quattrone D, Tofani L, Tujjar O, Villa G, Romano SM, De Gaudio AR. Accuracy of invasive arterial pressure monitoring in cardiovascular patients: an observational study. Crit Care. 2014 Nov 30;18(6):644. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0644-4. PMID: 25433536; PMCID: PMC4279904.
12. Persona P, Valeri I, Saraceni E, De Cassai A, Calabrese F, Navalesi P. Cardiac Output Evaluation on Septic Shock Patients: Comparison between Calibrated and Uncalibrated Devices during Vasopressor Therapy. J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 9;10(2):213. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020213. PMID: 33435270; PMCID: PMC7826755.
13. Scolletta, S., Bodson, L., Donadello, K. et al. Assessment of left ventricular function by pulse wave analysis in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 39, 1025–1033 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-2861-8